Sleep apnoea or as it is more commonly thought of – snoring, is a very common issue in households. This post will discuss sleep apnoea so you understand it and the relationship to snoring as well as the best treatment options for it and snoring.
Snoring is certainly annoying and disruptive, but what about when snoring becomes dangerous?
While snoring has significant health impacts, from tiredness to memory issues, relationship implications to moodiness, and even the development of chronic diseases, sometimes snoring is itself a symptom of a more serious health condition like sleep apnoea.
What is Snoring?
Snoring is a very common issue that occurs as a direct result of narrowed airways or breathing passages. The soft tissues within the neck relax and the airways of the throat collapse, making the tissues of the throat vibrate as you try to breathe in. Common causes of snoring include:
- Enlarged uvula, adenoids, or tonsils
- Deviated nasal septum
- Nasal congestion or sinus issues
- Being overweight (especially neck fat)
- Alcohol consumption
- Sleeping on your back
The disruption to quality sleep that snoring causes can create an array of ongoing issues, such as sleepiness, irritability, headaches, stress, and even major conditions like high blood pressure and obesity.
What is Sleep Apnoea?
Much more significant than regular snoring, sleep apnoea is a serious medical condition. Proper sleep apnoea treatment is imperative. Snoring is an important symptom of sleep apnoea, but not every snorer will have apnoea.
Sleep apnoea is characterized by repeated partial or complete collapse or blockage of the airway, causing shallow breathing which briefly stops. The pauses in breathing may last anywhere between a few seconds to minutes, and these may happen many hundreds of times a night. During these pauses in breathing, blood oxygen levels drop and sleep is interrupted briefly (for as little as three seconds) so that breathing recommences. As breathing resumes, the person will snort, choke, or gasp for air.
How Does Sleep Apnoea Differ from Regular Snoring?
People who snore generally do not experience complete breathing disruption. Sufferers of sleep apnoea, however, stop breathing many times per hour – as often as once every two minutes or more. Consequences of this include:
- Oxygen deprivation to the brain and body
- Very poor sleep quality
- Daytime sleepiness, irritability, and poor cognitive and physical performance
- Morning headaches
- Compromised safety on the road and in the workplace
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Higher risk of stroke, heart attack, diabetes, cancer, and obesity
Sleep Apnoea Treatment & Diagnosis – Options and Considerations
Sleep apnoea occurs in people of all ages, however, it is much more common in people who are overweight. Most sufferers are unaware they have sleep apnoea – they just suspect that they snore and, likely, feel unrefreshed during the day.
As many as 10% of Australians are believed to suffer from undiagnosed obstructive sleep apnoea. (Source: NCBI) It is more common in and after middle age, and more likely for men than women, with rates as high as 49% in men between 40-69 years and as many as 62% of men aged over 70. Children and younger people who experience the problem are usually found to have enlarged tonsils or adenoids. Women are at higher risk following menopause.
Diagnosis of sleep apnoea is not simple, and you must see your doctor. They may suggest:
- Keeping a sleep diary, noting times of going to sleep, waking, napping, and how you feel throughout the day and evening.
- Keeping a record of your snoring, based on reporting from your partner or other household members.
- Physical examination to check your nose, mouth, throat, especially your tonsils and uvula.
- Professional, medical sleep studies performed in a sleep lab or sleep centre or using a portable, home-based monitor.
Sleep apnoea treatment depends on the severity of the problem. For some, losing weight, minimizing alcohol consumption, and sleeping on the side is enough to alleviate the issue adequately. Most, however, require more targeted treatment. This may include:
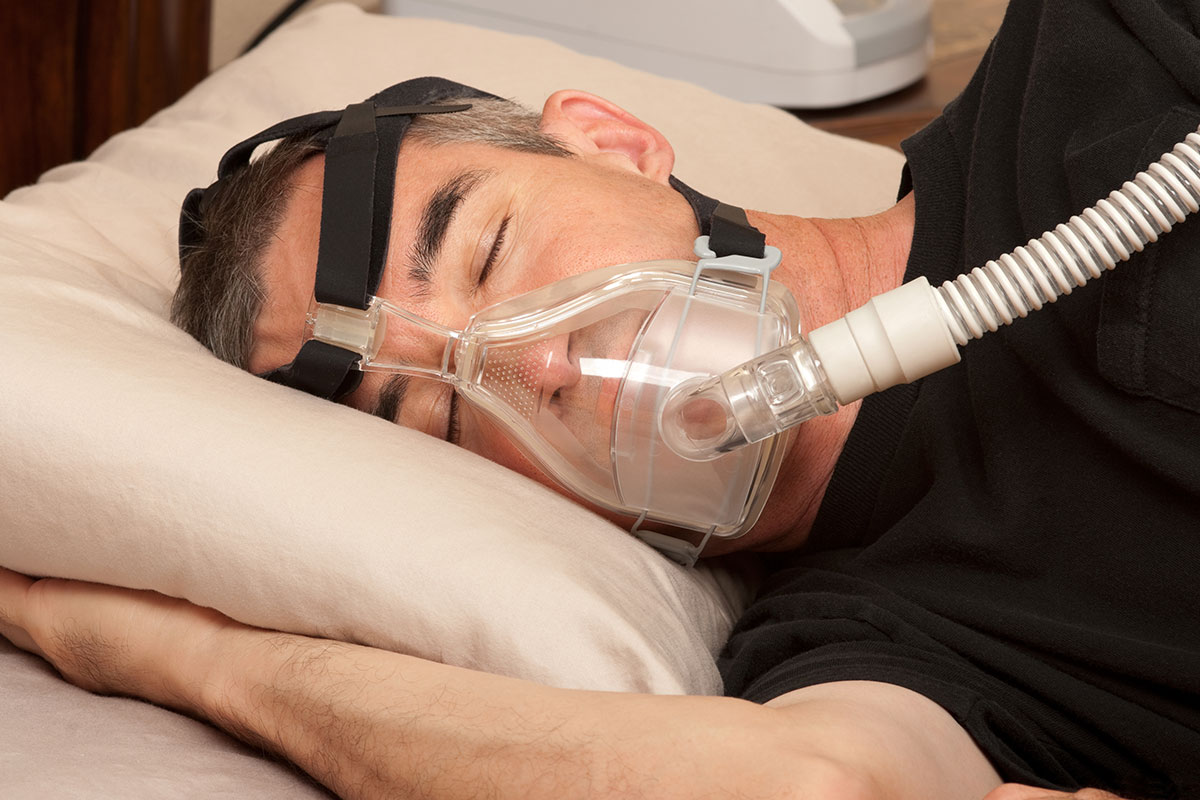
- CPAP or continuous positive airway pressure uses a face or nasal mask attached to a small pump. It takes room air and gently pressurizes it to help hold the tissues of the throat open during sleep. It is an effective way to control symptoms and minimize the effects of sleep apnoea.
- Surgery may be recommended to remove oversized tonsils and adenoids, an enlarged uvula, or to repair a deviated nasal septum.
- Losing weight is important if you are overweight and experience sleep apnoea. Likewise, avoiding sleeping medications and alcohol is highly recommended.
Learn About SnoreMD – The Antidote to Snoring
Sleep apnoea is a problem for sufferers and their families. It requires a medical diagnosis and specialist medical treatment.
If, however, you experience regular snoring, there are a lot of ways you can address it and making small but significant changes to your everyday life may minimise your risks.
One medically proven solution to help stop snoring is SnoreMD. This anti-snoring device is used worldwide, and SnoreMD is an Australian brand. When worn in the mouth during sleep, SnoreMD gently, yet comfortably, repositions the lower jaw to modify the position of the tongue and soft palate, and with it the behaviour of the lower jaw muscles. This helps to keep the airways open for easier breathing and less snoring.
SnoreMD is:
- Biomedically engineered and manufactured to the highest Australian standards
- Medically proven to be effective
- Micro-Adjustable, comfortable, and safe to use
- Affordable and reusable
- Recommended by doctors, dentists, pharmacists, and sleep specialists
- Carries no negative side effects
- Will not disrupt sleep
SnoreMD is the perfect, simple snoring solution. Learn more about SnoreMD here or buy today.


